In the fast-paced world of education, academic stress has become a common companion for students of all ages. The pressure to excel, meet deadlines, and perform well in exams can create a burden that weighs heavily on their young shoulders. But what exactly is academic stress? Beyond the surface-level understanding, it encompasses a complex web of challenges, emotions, and expectations that students face in their academic pursuits.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into the concept of academic stress, exploring its causes, effects, and strategies to manage and overcome it. So, grab a seat, take a deep breath, and let’s navigate the intricate landscape of academic stress together.
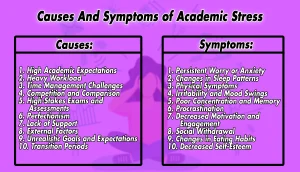
Causes And Symptoms of Academic Stress:
Causes:
1. High Academic Expectations:
The pressure to meet high academic expectations set by parents, teachers, or oneself can contribute to academic stress. The desire to achieve top grades excel in exams, and secure future opportunities can be overwhelming.2. Heavy Workload:
An excessive workload, including multiple assignments, projects, and exams, within limited timeframes can lead to stress. Balancing academic responsibilities with other commitments adds to the pressure.3. Time Management Challenges:
Poor time management skills can contribute to academic stress. Procrastination, lack of organization, and difficulty prioritizing tasks can lead to last-minute cramming and increased stress levels.4. Competition and Comparison:
The competitive nature of education and the constant comparison with peers can generate stress. The fear of falling behind or not measuring up to others’ achievements can be a significant source of stress.5. High-Stakes Exams and Assessments:
Exams or assessments with high stakes, such as college entrance exams or standardized tests, can intensify academic stress. The weight placed on these evaluations amplifies the fear of failure and performance anxiety.6. Perfectionism:
Striving for perfection in academics can fuel stress. The need to constantly achieve flawless results and fear of making mistakes can lead to excessive self-criticism and increased stress levels.7. Lack of Support:
Inadequate support systems, such as limited access to academic resources, a lack of guidance from teachers or mentors, or minimal emotional support from family and friends, can contribute to academic stress.8. External Factors:
External factors such as financial pressures, family issues, personal health concerns, or other life stressors can indirectly impact academic performance and increase stress levels.9. Unrealistic Goals and Expectations:
Setting unrealistic goals or having unrealistic expectations of oneself can create immense stress. Putting undue pressure on achieving unattainable standards can lead to feelings of frustration and anxiety.10. Transition Periods:
Transitions, such as moving to a new school, starting college, or entering a challenging academic program, can be stressful due to adjustments in routines, social dynamics, and increased academic demands.Symptoms:
1. Persistent Worry or Anxiety:
Experiencing ongoing worry, anxiety, or feeling overwhelmed about academic performance, deadlines, or exams is a common symptom of academic stress.2. Changes in Sleep Patterns:
Academic stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling asleep, restless nights, or frequent waking up during the night.3. Physical Symptoms:
Headaches, stomachaches, muscle tension, and fatigue are physical symptoms that may manifest due to academic stress.4. Irritability and Mood Swings:
Increased irritability, mood swings, or heightened emotional reactions can be signs of academic stress.5. Poor Concentration and Memory:
Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or decreased ability to retain information is cognitive symptoms associated with academic stress.6. Procrastination:
Consistently delaying or avoiding academic tasks, despite knowing the consequences, can be a sign of academic stress.7. Decreased Motivation and Engagement:
Feeling demotivated, disinterested, or lacking enthusiasm for learning and academic activities can be indicators of academic stress.8. Social Withdrawal:
Withdrawing from social interactions, isolating oneself, or avoiding social events due to academic stress is a common behavior observed in stressed students.9. Changes in Eating Habits:
Significant changes in appetite, such as overeating or loss of appetite, can be related to academic stress.10. Decreased Self-Esteem:
Academic stress can negatively impact self-esteem, leading to feelings of inadequacy, self-doubt, or diminished confidence in one’s abilities.Impact On Learning And Coping Strategies
Impact on Learning:
1. Reduced Cognitive Performance:
Academic stress can hinder cognitive functions, including attention, memory, and information processing. Students may struggle to concentrate and retain information effectively, leading to decreased learning outcomes.2. Impaired Problem-Solving Skills:
High levels of stress can impede problem-solving abilities, making it challenging for students to approach complex tasks or find innovative solutions to academic challenges.3. Decreased Motivation and Engagement:
Academic stress can dampen students’ motivation and engagement in learning. The pressure and anxiety associated with academic demands may result in a loss of interest and enthusiasm, hindering active participation in the learning process.4. Negative Impact on Academic Performance:
Unmanaged academic stress can have a detrimental effect on academic performance. It may lead to lower grades, decreased productivity, and a decline in overall achievement.Coping Strategies:
1. Time Management:
Effective time management helps students prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and allocate sufficient time for studying assignments, and relaxation. Developing a schedule and sticking to it can reduce stress and enhance productivity.2. Seek Support:
It is important for students to seek support from teachers, mentors, or counselors when experiencing academic stress. They can provide guidance, offer resources, and assist in developing strategies to cope with academic challenges.3. Practice Stress-Reduction Techniques:
Engaging in stress-reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness, can help students relax their minds and bodies, promoting a sense of calm and well-being.4. Break Tasks into Manageable Steps:
Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps can make them less overwhelming. Students can focus on one step at a time, which helps reduce stress and enhances productivity.5. Establish a Supportive Study Environment:
Creating a conducive study environment free from distractions can improve focus and concentration. Having a dedicated study space, organizing study materials, and minimizing interruptions can enhance learning efficiency.6. Take Breaks and Practice Self-Care:
Taking regular breaks during study sessions is crucial for mental rejuvenation. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and self-care, such as exercising, spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies, or getting enough sleep, helps alleviate stress and maintain well-being.7. Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Habits:
A healthy lifestyle contributes to better stress management. Students should prioritize regular exercise, maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and avoid excessive caffeine or unhealthy coping mechanisms like substance abuse.8. Foster a Supportive Social Network:
Building connections with peers who share similar academic experiences can provide a sense of camaraderie and support. Sharing concerns, studying together, and seeking assistance when needed can alleviate stress and foster a positive learning environment.9. Practice Positive Self-Talk:
Encouraging self-talk and positive affirmations can help students combat negative thoughts and build self-confidence. Reminding oneself of past achievements, acknowledging efforts, and focusing on personal growth can reduce stress and enhance motivation.10. Set Realistic Expectations:
Setting realistic expectations for oneself and acknowledging that perfection is not attainable in every aspect of academics can alleviate stress. Embracing mistakes as learning opportunities and celebrating progress rather than solely focusing on outcomes can foster a healthier mindset.Tips To Help You Effectively Manage Your Studies And Exams While Avoiding The Accumulation of Academic Stress.
1. Don’t let it build up:
It is important not to let academic stress accumulate over time. Addressing and managing stress as it arises can prevent it from becoming overwhelming. This involves acknowledging your feelings, recognizing signs of stress, and taking proactive steps to address them.2. Ask for help if you need it:
When facing academic challenges or feeling overwhelmed, it is essential to reach out and ask for help. Seeking assistance from teachers, mentors, or classmates can provide valuable guidance, clarification, and support.3. Look after yourself:
Taking care of your physical, mental, and emotional well-being is crucial to managing academic stress. Prioritize self-care activities such as maintaining a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, and getting sufficient sleep.The Negative Impact of Academic Stress
Academic stress can have several negative impacts on students’ well-being, academic performance, and overall quality of life. Here are some of the negative effects of academic stress:
1. Mental Health Issues:
High levels of academic stress can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and burnout. The constant pressure to perform well and meet academic expectations can take a toll on students’ mental well-being, leading to emotional distress and a decline in overall mental health.2. Physical Health Problems:
Academic stress can manifest in physical health problems. Students experiencing high levels of stress may suffer from headaches, fatigue, insomnia, weakened immune systems, and gastrointestinal issues. The body’s response to chronic stress can disrupt its natural balance and lead to various health complications.3. Reduced Learning and Retention:
Excessive stress can impair learning and memory retention. When students are overwhelmed by stress, their ability to concentrate, process information, and retain knowledge can be significantly diminished. This can hinder academic performance and result in decreased learning outcomes.4. Decreased Motivation and Engagement:
Academic stress can dampen students’ motivation and enthusiasm for learning. The constant pressure and fear of failure can lead to a loss of interest and disengagement from academic activities. As a result, students may not fully participate in class, neglect assignments, or lose their passion for learning.5. Strained Relationships:
Academic stress can put a strain on relationships with family, friends, and peers. Students overwhelmed by stress may withdraw socially, experience heightened irritability or mood swings, and struggle to maintain healthy connections. This can lead to feelings of isolation and further exacerbate their stress levels.6. Impaired Decision-Making Skills:
Stress can impair students’ decision-making abilities. When under significant stress, individuals may struggle to think clearly, weigh options effectively, and make rational choices. This can have consequences in academic settings, such as difficulty in selecting appropriate courses, setting realistic goals, or making sound academic decisions.7. Negative Attitudes Towards Learning:
Prolonged exposure to academic stress can create negative attitudes and associations with learning. Students may develop a fear of failure, harbor self-doubt, or develop a mindset of academic inadequacy. These negative attitudes can impact their self-esteem, confidence, and overall approach to education.8. Reduced Overall Well-being:
Academic stress can take a toll on students’ overall well-being, leading to a diminished quality of life. The constant pressure and anxiety associated with academic demands can prevent students from enjoying a balanced lifestyle, engaging in extracurricular activities, pursuing personal interests, or maintaining healthy relationships.
It is crucial to address and manage academic stress effectively to mitigate these negative impacts. Implementing stress management strategies, seeking support, and prioritizing self-care can help students maintain their well-being and achieve academic success in a healthier and more balanced way.
How Does Academic Stress Affect Students?
Academic stress can significantly affect students in various ways, creating a ripple effect that impacts their overall well-being, academic performance, and quality of life. It’s essential to understand how academic stress takes its toll on students’ lives and the challenges they face. Let’s explore the ways academic stress affects students:
1. Mental and Emotional Exhaustion:
Academic stress can leave students feeling mentally and emotionally drained. The constant pressure to perform well, meet deadlines, and excel academically can overwhelm their minds, leading to exhaustion and a sense of emotional depletion. This state of mental fatigue can make it challenging to concentrate, retain information, and engage effectively in their studies.2. Anxiety and Worry:
Excessive academic stress often triggers anxiety and worry in students. The fear of failure, the pressure to meet expectations, and the intense competition can create a constant sense of unease. Students may experience racing thoughts, restlessness, and a heightened sense of apprehension, making it difficult for them to focus on their studies or perform at their best.3. Self-Doubt and Imposter Syndrome:
Academic stress can breed self-doubt and feelings of inadequacy in students. The constant comparison to peers, the fear of not measuring up, and the weight of expectations can lead students to question their abilities and suffer from imposter syndrome. This internal struggle can undermine their confidence and hinder their academic progress.4. Physical Health Challenges:
The impact of academic stress extends beyond the mental and emotional realms, affecting students’ physical health as well. Prolonged stress can manifest in physical symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, sleep disturbances, weakened immune systems, and even exacerbate pre-existing health conditions. The toll on their physical well-being further complicates their ability to cope with academic demands.5. Social Withdrawal and Isolation:
Students under significant academic stress may withdraw from social interactions and isolate themselves. The overwhelming workload, time constraints, and the need to focus on academic priorities can lead to reduced social engagement. This isolation can deprive students of valuable support systems, meaningful connections, and the emotional nourishment that comes from social interactions.6. Burnout and Loss of Passion:
Unmanaged academic stress can push students to the point of burnout. The constant pressure, relentless studying, and lack of balance can drain their energy and enthusiasm for learning. What was once a passion for education may transform into a sense of monotony or even resentment, diminishing their motivation and compromising their long-term educational goals.7. Strained Relationships:
Academic stress can strain relationships with family, friends, and peers. The time and energy dedicated to academic pursuits may leave little room for maintaining healthy connections. Students may experience conflicts with loved ones, feel misunderstood, or struggle to balance their academic commitments with their social lives, further adding to their stress levels.How To Reduce Academic Stress?
Reducing academic stress is essential for students to maintain their well-being and perform at their best. Here are some effective strategies and techniques to help alleviate academic stress:
1. Prioritize and Organize:
Start by prioritizing your tasks and creating a realistic schedule. Break down your workload into manageable chunks and allocate time for each task. This helps create a sense of structure and control, reducing feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.2. Time Management:
Develop effective time management skills to ensure a balanced approach to your studies. Set specific goals for each study session, use tools like timers or productivity apps, and avoid procrastination. By managing your time efficiently, you can prevent last-minute cramming and reduce stress levels.3. Practice Self-Care:
Make self-care a priority to nurture your physical and mental well-being. Engage in activities that help you relax and recharge, such as exercise, meditation, hobbies, or spending time with loved ones. Taking care of yourself reduces stress, improves focus, and enhances overall resilience.4. Seek Support:
Don’t hesitate to reach out for help when needed. Talk to your teachers, classmates, or school counselors if you’re struggling with certain subjects or feeling overwhelmed. They can provide guidance, clarification, or additional resources to support your academic journey.5. Breaks and Rest:
Incorporate regular breaks into your study routine. Taking short breaks allows your mind to recharge and improves focus when you return to studying. Also, prioritize sufficient sleep to enhance concentration, memory retention, and overall cognitive function.6. Positive Mindset and Self-Talk:
Foster a positive mindset by reframing negative thoughts and practicing self-compassion. Replace self-criticism with positive affirmations and realistic self-talk. Remind yourself of your abilities, strengths, and past successes to boost your confidence and reduce stress.7. Effective Study Techniques:
Explore different study techniques and find what works best for you. Experiment with methods such as active learning, summarizing information, creating visual aids, or teaching concepts to others. Finding engaging and effective study strategies can enhance your understanding and reduce stress.8. Balance and Leisure Activities:
Make time for activities outside of academics that bring you joy and relaxation. Engage in hobbies, pursue creative outlets, or participate in sports or other recreational activities. Finding a balance between studying and leisure activities helps alleviate stress and prevents burnout.9. Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating nutritious meals, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive caffeine or sugary foods. A well-nourished body supports cognitive function and reduces physical stress. Also, consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or yoga into your routine.10. Perspective and Mindfulness:
Practice mindfulness to stay present and focus on the task at hand. Avoid getting caught up in future worries or past mistakes. Cultivate gratitude and take moments to appreciate your progress, small achievements, and the joy of learning.How Does Academic Stress Contribute To Cheating?
Academic stress can be a contributing factor to cheating among students. When students face excessive pressure to perform well academically, they may feel overwhelmed and resort to dishonest means, such as cheating, to cope with the demands. Here are some ways in which academic stress can contribute to cheating:
1. Fear of Failure:
The fear of failure can drive students to engage in cheating behaviors. When the stakes are high and the pressure to excel is intense, some students may perceive cheating as a way to secure better grades or avoid disappointing themselves or others. The fear of academic failure can lead them to compromise their integrity in an attempt to maintain a sense of achievement.2. Competitive Environment:
In highly competitive academic settings, where students are constantly compared to their peers, the pressure to outperform others can be overwhelming. The intense competition can create an environment where students feel compelled to resort to cheating as a means to gain an advantage and secure a higher rank or position.3. Time Constraints and Workload:
A heavy workload and time constraints can contribute to academic stress, leaving students feeling overwhelmed and desperate to meet deadlines. In such situations, students may be tempted to engage in cheating to save time and complete assignments or exams quickly, as they perceive it as the only way to cope with the demanding academic demands.4. Perceived Lack of Support:
When students feel unsupported or believe that their academic challenges are not adequately addressed, they may turn to cheating as a coping mechanism. If they perceive that their educational environment does not provide the necessary resources, guidance, or support, they may feel compelled to resort to dishonest practices to level the playing field or bridge the perceived gaps.5. Unrealistic Expectations:
Unrealistic academic expectations, either self-imposed or imposed by external sources such as parents or educators, can create immense pressure on students. When the expectations set for them seem unattainable, students may feel compelled to cheat to meet those expectations or avoid potential negative consequences, such as disappointing others or damaging their academic reputation.6. Lack of Ethical Education:
Insufficient emphasis on ethical education and academic integrity can contribute to a culture where cheating is more likely to occur. When students are not adequately educated about the importance of honesty and the consequences of cheating, they may be more inclined to engage in dishonest practices when faced with academic stress.Final Thoughts:
Academic stress is a significant issue that affects students’ well-being, academic performance, and overall quality of life. We explored various aspects of academic stress, including its causes, symptoms, negative impacts, and ways to manage and reduce it effectively.
It is crucial for students, educators, and parents to prioritize the well-being of students and implement strategies to manage academic stress effectively. By doing so, we can create a healthier learning environment that fosters growth, resilience, and success.